Digital transformation is one of the top priorities in the agenda of the European Union. The EU’s main goal is to implement policies that will offer new digital opportunities to businesses and consumers like for instance assisting in the digitization of public services, fostering an open and democratic society, creating new opportunities for businesses or improve the digital skills of workers around Europe.
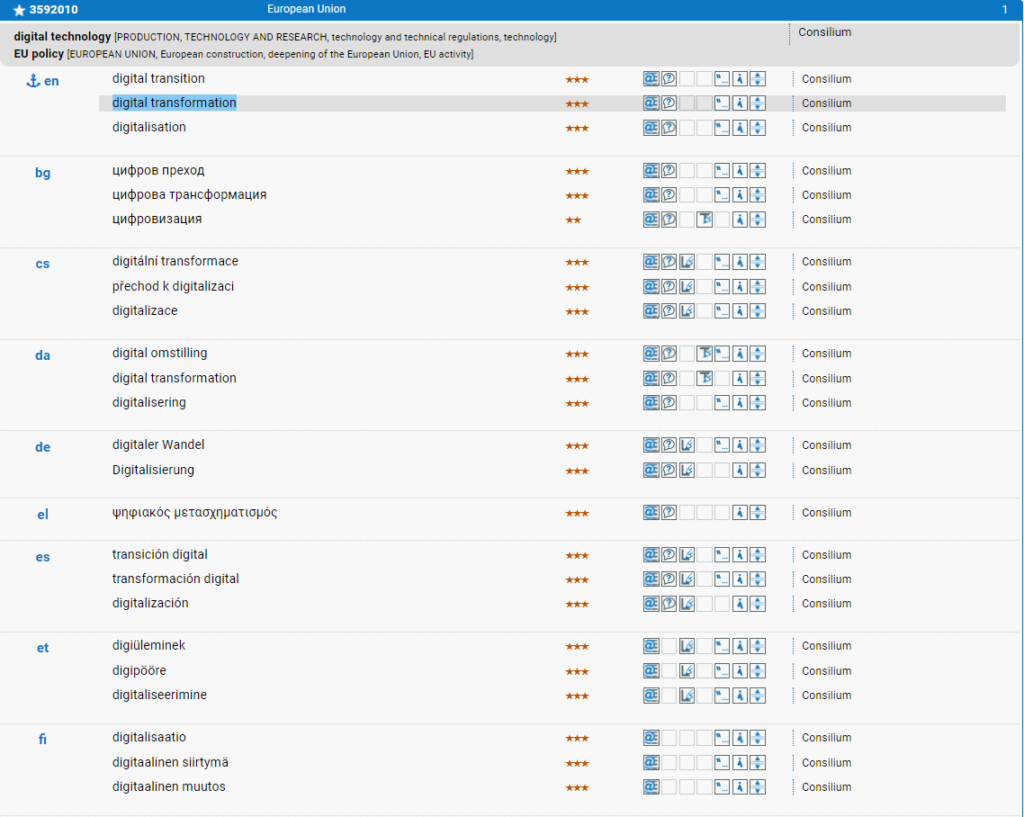
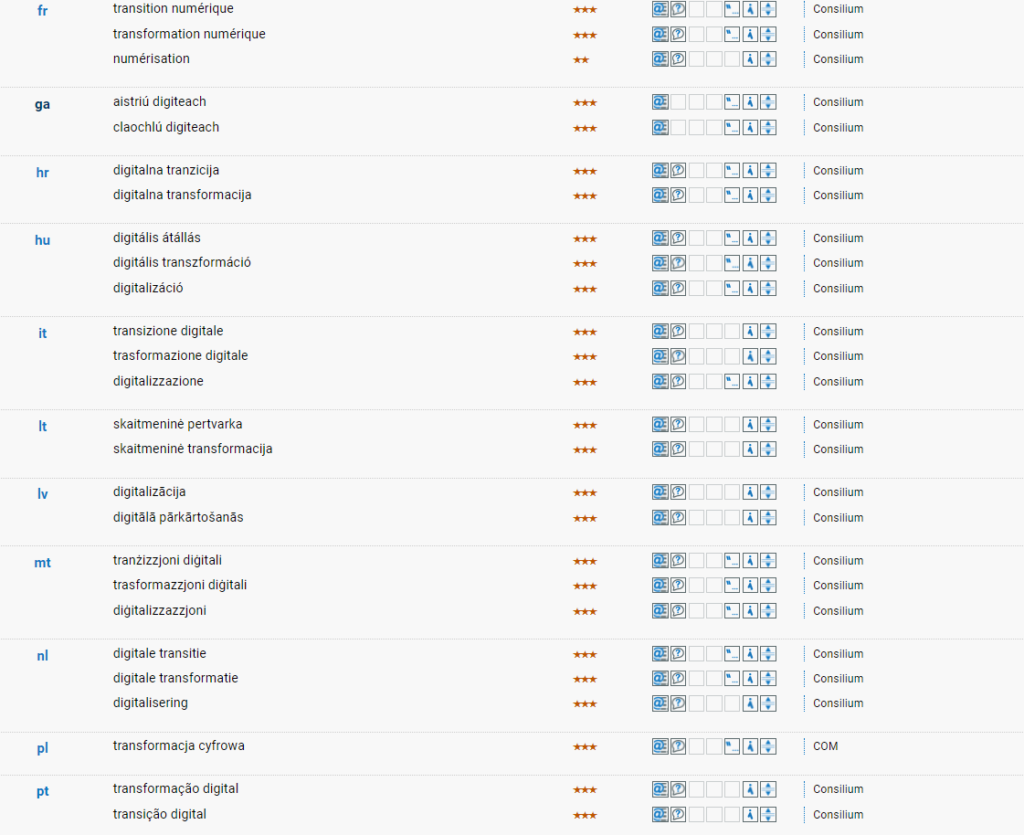
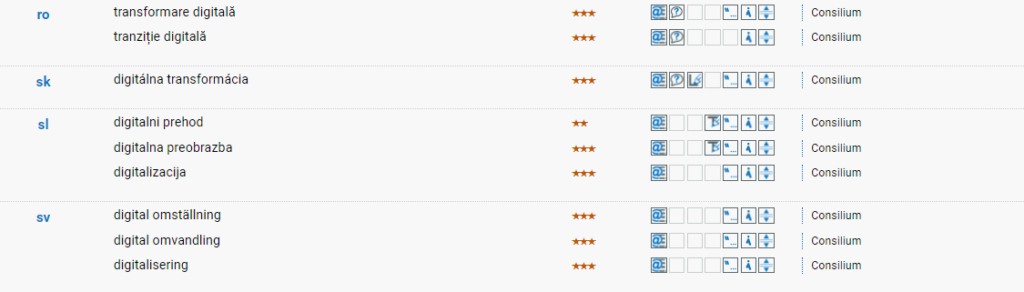
What is Digital Transformation?
Digital transformation refers to the adoption of digital technologies by companies and also the effect of technologies in society. Sectors such as transport, telecommunications, agriculture, financial services, healthcare and energy are some of the sectors deeply affected by technologies such as cloud computing, Internet of Things (IoT) or Artificial Intelligence (AI). The implementation of digital transformation technologies could assist in the waste and emission reductions, as well as the development of new services and products for consumers and, in addition, help companies in improving their competitive advantages in the market.
Digital Transformation Initiatives by the EU
Especially during the Covid-19 pandemic, digital transformation created the need for more drastic measures that will enable Europe to recover fast and gain back its position in the global economy. During the pandemic it was noticed that 42% of all EU citizens lack basic digital skills. In addition, 41% of people living in rural areas don’t have access to high-capacity networks, compared to 13% of people living in urban areas.
As a result, various initiatives, investment and infrastructure programmes such as the Digital Europe Programme, the EU’s Plan for Economic Recovery, the Research & Innovation-centred Horizon Europe and also the Connecting Europe Facility were created in order to ensure that both citizens and businesses benefit equally from the new technological advancements.
The European new tech-approach of the European Commission is based on three core pillars:
People-centric Technology
The first pillar of the Commission’s digital strategy deals with the digital literacy of the European citizens, the protection from cyber threats or hacking attacks, artificial intelligence development and broadband connectivity for schools, healthcare or hospitals.
Digital Economy
The second pillar focuses on making digital economy more fair and competitive. The goals of the EU’s digital strategy is to enable innovation in start-ups and small companies, as Members of the European Parliament have pointed out the importance of adopting digital transformation tactics such as artificial intelligence (AI) in the private and public sectors especially for Small Medium Enterprises (SMEs) as well. Furthermore, topics such as the Digital Services Act, fair competition among companies, protection of high-quality and sensitive data and EU regulations regarding digital economy are a priority in order to create a fair and democratic digital economy.
Open and Sustainable Society
The protagonist of the third pillar of EU’s digital strategy is sustainability. The goals include the reduction of the digital sector’s carbon emissions, the usage of technology in order to become climate-neutral by 2050, along with the creation of the European Health Data Space that will stimulate research, diagnosis and treatments.
Nonetheless, EU lawmakers and EU institutions need to take seriously into consideration the obstacles and challenges that exist before proposing effective, fruitful and innovative digital solutions with the aim to achieve fair digital transformation for all European citizens and businesses. Digital transformation is the door to the future that creates endless opportunities for a safer, more digital and more sustainable Europe and digital economy in the 21st century.
References:
Digital transformation in the EU | News | European Parliament. 2022. Digital transformation in the EU | News | European Parliament. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/news/en/headlines/priorities/digital-transformation. [Accessed 08 March 2022].
Digital transformation: importance, benefits and EU policy | News | European Parliament. 2022. Digital transformation: importance, benefits and EU policy | News | European Parliament. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/news/en/headlines/priorities/digital-transformation/20210414STO02010/digital-transformation-importance-benefits-and-eu-policy. [Accessed 08 March 2022].
The Parliament Magazine. 2022. Why Europe must lead the digital transformation. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.theparliamentmagazine.eu/news/article/why-europe-must-lead-the-digital-transformation. [Accessed 08 March 2022].
MEPs want more support for digital innovation and AI applications | News | European Parliament. 2022. MEPs want more support for digital innovation and AI applications | News | European Parliament. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/news/en/press-room/20210517IPR04133/meps-want-more-support-for-digital-innovation-and-ai-applications. [Accessed 08 March 2022].
European Commission – European Commission. 2022. Shaping Europe’s digital future | European Commission. [ONLINE] Available at: https://ec.europa.eu/info/strategy/priorities-2019-2024/europe-fit-digital-age/shaping-europe-digital-future_en. [Accessed 08 March 2022].

Written by Ioanna Mavridou
Ioanna holds a Bachelor’s degree in Translation from the Ionian University in Corfu and has also studied her Master’s in Communication at Gothenburg University in Sweden. A digital communications enthusiast, she has completed a professional Social Media & Digital Marketing certification. She speaks Greek, English, Swedish, German and Russian. She is a Communications Trainee at the Terminology Coordination Unit of the European Parliament.