Carbon footprint (also known as CO2 footprint) refers to the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions that are generated through human activities, such as transportation, energy production, and manufacturing. It is a significant environmental concern because these emissions contribute to climate change.
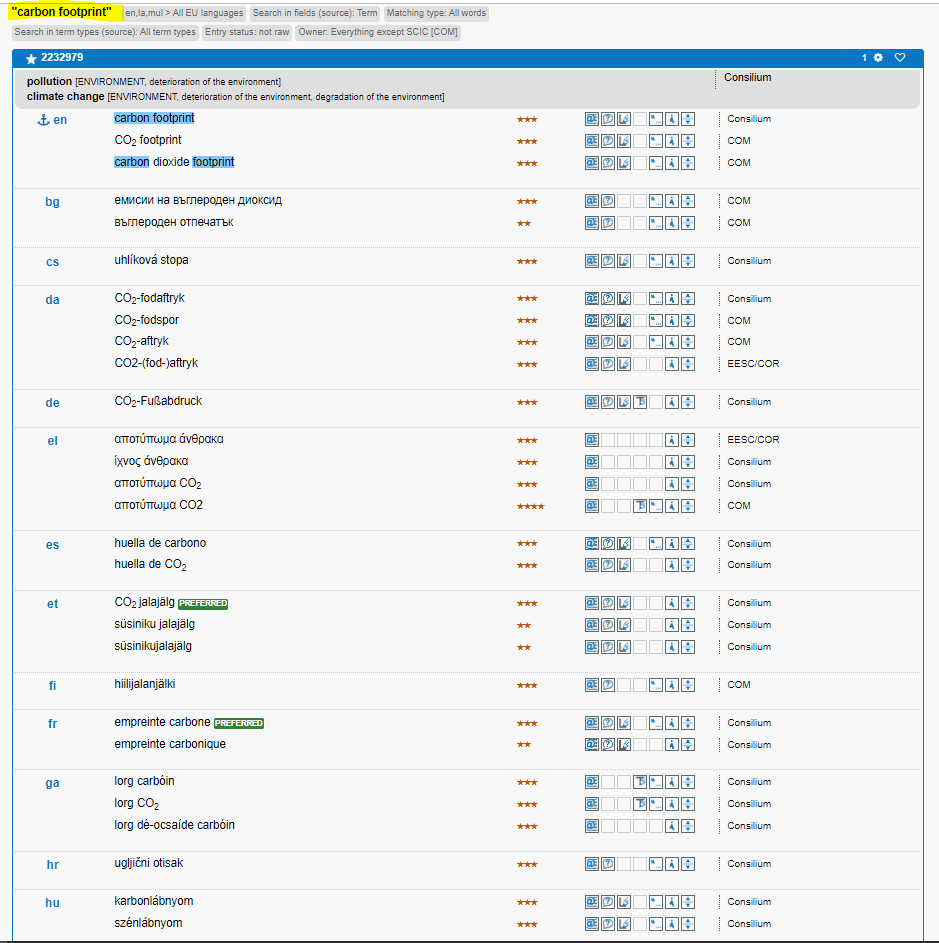
In IATE, this term is defined as “measure of the carbon emissions of a particular individual, organisation, community or product, implying the environmental impact of those carbon emissions”.
The European Union has been a leader in the fight against climate change, recognizing the importance of reducing carbon footprints in order to achieve sustainable development. The EU has implemented policies and legislation aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting the use of renewable energy sources.
One example of EU policies in this area is the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS), which is the world’s first and largest carbon trading system. This system creates a market for companies to trade carbon credits, encouraging them to reduce their emissions and incentivizing the development of low-carbon technologies.
Another important EU policy is the Renewable Energy Directive, which aims to increase the share of renewable energy sources in the EU’s energy mix. This directive sets binding targets for member states to achieve by 2030, encouraging investment in renewable energy infrastructure and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Overall, the EU’s focus on reducing carbon footprints is essential to protecting the environment and combatting climate change. By implementing policies and legislation aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, the EU is leading the way towards a more sustainable future.
Related terms: carbon neutrality (IATE ID no. 3566666), life cycle carbon footprint (IATE ID no. 3592094).
References
Bagchi, Chandreyee and Velten, Eike Karola (2014). “The EU Emissions Trading System: Regulating the Environment in the EU”. Climate Policy Info Hub, 13 May. Online available at: http://climatepolicyinfohub.eu/eu-emissions-trading-system-introduction
European Parliament (2023). “Climate change: the greenhouse gases causing global warming”, News, 23 March, accessed April 2023.Online available at: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/news/en/headlines/society/20230316STO77629/climate-change-the-greenhouse-gases-causing-global-warming
European Parliament (n.d.). “Reducing our ecological footprint. Applying EMAS at the European Parliament”. Accessed April 2023. Online available at: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/about-parliament/en/organisation-and-rules/ecological-footprint
Masterson, Victoria (2022). “The European Union has cut greenhouse gas emissions in every sector”, World Economic Forum, 29 September, accessed April 2023.
Written by Victoria Saura Montesinos
 | Born in Murcia, Spain, her academic background includes a Double Degree in Linguistics and Applied Languages and English Studies at the University of Cadiz and Loughborough University (Erasmus+), and a Master’s degree in Spanish as a Foreign Language (Mid Atlantic University). With the aim of continuing her research career, Victoria is currently doing a PhD in Applied Linguistics, with a scientific interest in Terminology and Specialised Communication, Lexical Semantics, Corpus Linguistics and Digital Linguistics. |