The idea of herd immunity as a possible answer to the COVID-19 pandemic has triggered heated debate, but what is herd immunity and how does it work?
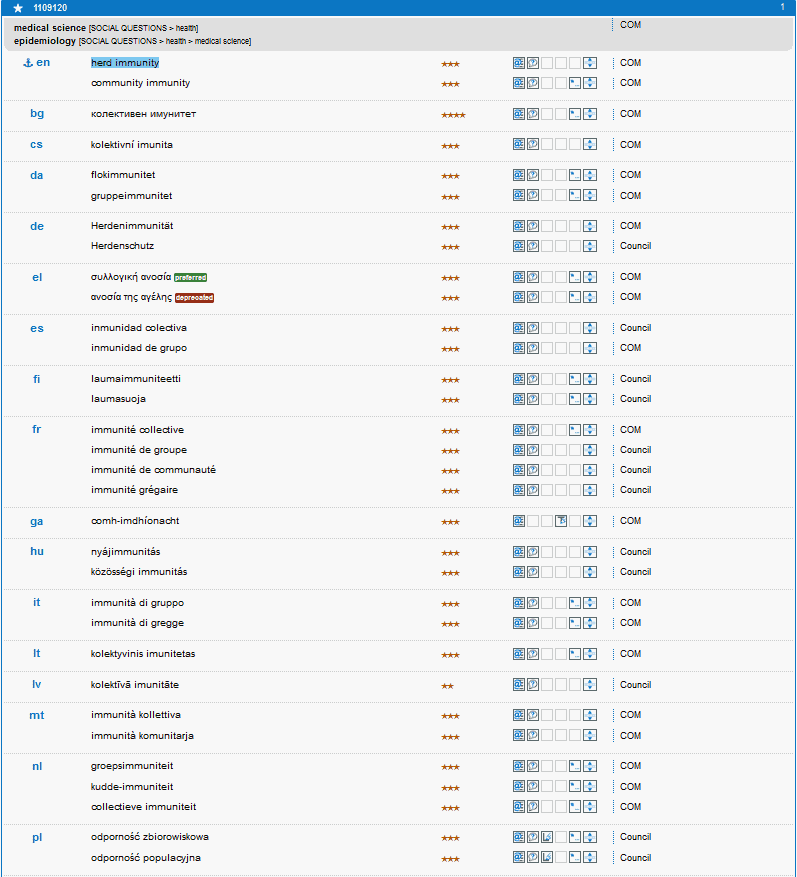
Herd immunity (also called herd effect, community immunity, population immunity, or social immunity) occurs when a large portion of a community (known as “the herd”) becomes immune to a disease, whether through vaccination or previous infection. In a population in which a large proportion of individuals possess immunity, such people being unlikely to contribute to disease transmission, chains of infection are more likely to be disrupted, which either stops or slows the spread of disease. To put it more simply: once the level of immunity passes a certain threshold, then the pandemic will start to die out because there are not enough new people to infect.

While no country claims to be pursuing herd immunity as a strategy, some have taken a more relaxed approach to containing the coronavirus. Sweden has been the poster child for herd immunity, even if it is not the country’s official policy. While other Scandinavian countries used lockdowns and broad public restrictions to stop the spread of COVID-19, Sweden opted for more mild interventions and personal responsibility to slow the spread. As a result, they reported up to 1,699 new coronavirus cases. However, according to Anders Tegnell, a Swedish physician specializing in Infectious disease and the current state epidemiologist of Sweden, the rise in new cases is due to a recent bump in testing and that Sweden is seeing a relatively low number of admissions to intensive care units, along with a decline in COVID-19 deaths.
To achieve herd immunity, each infected person must, on average, infect less than one person. Once the transmission rate drops below one, a community has reached herd immunity. So far, 0.14% of the population has been tested positive to COVID-19.
Sources
Mayo Clinic, Herd immunity and COVID-19 (coronavirus): What you need to know https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/coronavirus/in-depth/herd-immunity-and-coronavirus/art-20486808
Quanta Magazine, The tricky math of herd immunity for COVID-19 https://www.quantamagazine.org/the-tricky-math-of-covid-19-herd-immunity-20200630/
APIC (Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology), Herd Immunity https://apic.org/monthly_alerts/herd-immunity/
Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, What is herd immunity and how can we achieve it with COVID-19? https://www.jhsph.edu/covid-19/articles/achieving-herd-immunity-with-covid19.html
 Written by Eva Gozlan. She is currently validating her Master’s degree in Translation and International Communication at ISIT School.
Written by Eva Gozlan. She is currently validating her Master’s degree in Translation and International Communication at ISIT School.